Swingでグラフィックスを用いるサンプル
グラフを描く
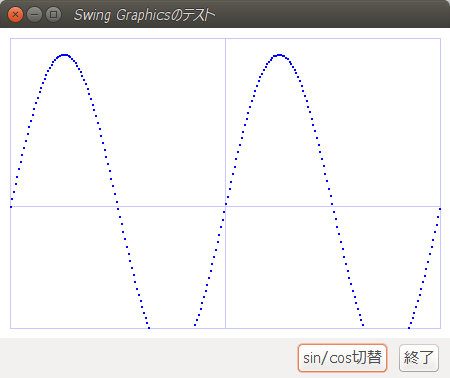
実数座標 (x,y) を、画面上のピクセル座標に変換してグラフをプロットする例。 ウインドウを伸縮させると、描画エリアのサイズも変化するので、それに合わせてpaintComponentメソッドが呼ばれて自動的に画面が再描画される。
メイン クラスのコード
public class SwingGraphics01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setTitle("Swing Graphicsのテスト");
frame.setSize(450, 350);
// 親コンテナ(この中に、子コンテナとしてpanel2つを上下配置する)
Container container = frame.getContentPane();
container.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
frame.setContentPane(container);
// ダイアログ上部のグラフィックエリアの定義
GraphicsJPanel01 panel_1 = new GraphicsJPanel01();
panel_1.SetXyRange(-3.14*2, 3.14*2, -0.8, 1.1);
container.add(panel_1, BorderLayout.CENTER);
// ダイアログ下部のボタン エリアの定義
JPanel panel_2 = new JPanel();
panel_2.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT, 10, 5));
JButton buttonGraphicDraw = new JButton("sin/cos切替");
panel_2.add(buttonGraphicDraw);
JButton buttonClose = new JButton("終了");
panel_2.add(buttonClose);
container.add(panel_2, BorderLayout.PAGE_END);
// 「終了」ボタンの処理
buttonClose.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
frame.setVisible(false);
frame.dispose();
}
});
// 「sin, cos 切替」ボタンの処理
buttonGraphicDraw.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
panel_1.ToggleSinCos();
// グラフの強制再描画
panel_1.repaint();
}
});
// 実行環境OSにあったUIを適用する
try {
// UIManager.setLookAndFeel("com.sun.java.swing.plaf.gtk.GTKLookAndFeel");
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName());
// SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(panel);
SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(frame);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
// メイン ダイアログの表示
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
グラフィックス描画のためのクラス
public class GraphicsJPanel01 extends JPanel {
// sin または cos のグラフ描画の切替用フラグ
private int mode = 0;
// 描画領域の x, y 表示範囲
private double x1 = 0; // x_min
private double x2 = 1; // x_max
private double y1 = 0; // y_min
private double y2 = 1; // y_max
// 描画領域の上下・左右両端のボーダー幅
private int x_border = 10;
private int y_border = 10;
public GraphicsJPanel01() {
super();
this.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
// TODO 自動生成されたメソッド・スタブ
super.paintComponent(g);
DrawAxis(g); // 軸線を描く
DrawBorder(g); // グラフ外枠線を描く
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
for (double i = -3.14 * 2; i <= 3.14 * 2; i += 0.05) {
DrawPoint(g, i, this.mode == 0 ? Math.sin(i) : Math.cos(i));
}
}
public void ToggleSinCos() {
if (this.mode == 0)
this.mode = 1;
else
this.mode = 0;
}
/**
* 描画領域の x, y 表示範囲を設定する
*
* @param new_x1
* : (x min), xの表示範囲最小値
* @param new_x2
* : (x max), xの表示範囲最大値
* @param new_y1
* : (y min), yの表示範囲最小値
* @param new_y2
* : (y max), yの表示範囲最大値
*/
public void SetXyRange(double new_x1, double new_x2, double new_y1,
double new_y2) {
this.x1 = new_x1;
this.x2 = new_x2;
this.y1 = new_y1;
this.y2 = new_y2;
}
/**
* 実数 x を、描画領域の横座標(ピクセル)に変換する
*
* @param x
* : 実数
* @return
*/
private int ConvertX2W(double x) {
// 描画領域幅から、両端のボーダー幅を引く
int w = this.getWidth() - (x_border * 2);
// 実数を描画領域のピクセル座標に変換した値を返す
return ((int) ((x - x1) / (x2 - x1) * w) + x_border);
}
/**
* 実数 y を、描画領域の縦座標(ピクセル)に変換する
*
* @param y
* : 実数
* @return
*/
private int ConvertY2H(double y) {
// 描画領域高さから、上下のボーダー幅を引く
int h = this.getHeight() - (y_border * 2);
// 実数を描画領域のピクセル座標に変換した値を返す
return (h - (int) ((y - y1) / (y2 - y1) * h) + y_border);
}
/**
* 描画領域の外枠線を描く
*
* @param g
*/
private void DrawBorder(Graphics g) {
// 描画領域・高さから、それぞれボーダー幅を引く
int w = this.getWidth() - (x_border * 2);
int h = this.getHeight() - (y_border * 2);
// 描画領域の枠線を描く
g.setColor(new Color(200, 200, 255));
g.drawRect(x_border, y_border, w, h);
}
/**
* x=0およびy=0の軸線を描く
*
* @param g
*/
private void DrawAxis(Graphics g) {
g.setColor(new Color(200, 200, 255));
// x軸(横軸)を描く
g.drawLine(this.ConvertX2W(x1), this.ConvertY2H(0),
this.ConvertX2W(x2), this.ConvertY2H(0));
// y軸(縦軸)を描く
g.drawLine(this.ConvertX2W(0), this.ConvertY2H(y1),
this.ConvertX2W(0), this.ConvertY2H(y2));
}
/**
* 指定した実数座標(x,y)を、描画領域に点としてプロットする
*
* @param g
* @param x
* @param y
*/
private void DrawPoint(Graphics g, double x, double y) {
// 描画領域外のチェック
if (x < x1 || x2 < x || y < y1 || y2 < y)
return;
// 実数座標(x,y)を、画面描画する
g.drawRect(this.ConvertX2W(x), this.ConvertY2H(y), 1, 1);
}
}
ビットマップ画像を表示する
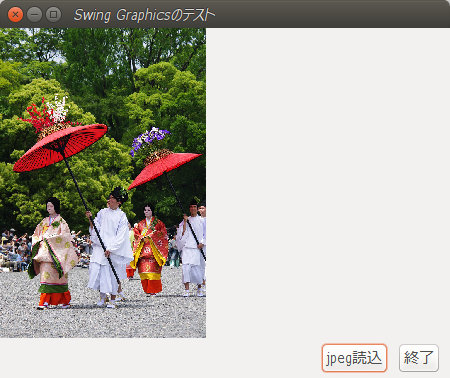
ウインドウの伸縮に合わせて、最適な縦横比を保持したスケーリング表示を行う。スケーリングは自動ではなく、ユーザが手動で計算してスケーリング結果の画像サイズをdrawImageで指定してやる必要がある。
メイン クラスのコード
public class SwingGraphics01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setTitle("Swing Graphicsのテスト");
frame.setSize(450, 350);
// 親コンテナ(この中に、子コンテナとしてpanel2つを上下配置する)
Container container = frame.getContentPane();
container.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
frame.setContentPane(container);
// ダイアログ上部のグラフィックエリアの定義
GraphicsJPanel02 panel_1 = new GraphicsJPanel02();
container.add(panel_1, BorderLayout.CENTER);
// ダイアログ下部のボタン エリアの定義
JPanel panel_2 = new JPanel();
panel_2.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT, 10, 5));
JButton buttonGraphicDraw = new JButton("jpeg読込");
panel_2.add(buttonGraphicDraw);
JButton buttonClose = new JButton("終了");
panel_2.add(buttonClose);
container.add(panel_2, BorderLayout.PAGE_END);
// 「終了」ボタンの処理
buttonClose.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
frame.setVisible(false);
frame.dispose();
}
});
// 「画像読込」ボタンの処理
buttonGraphicDraw.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JFileChooser dialog = new JFileChooser();
dialog.setFileFilter(new FileNameExtensionFilter(
"pngファイル (*.png)", "png", "PNG"));
dialog.setFileFilter(new FileNameExtensionFilter(
"jpegファイル (*.jpg)", "jpg", "jpeg", "JPG", "JPEG"));
dialog.setDialogTitle("画像ファイルを開く");
if (dialog.showOpenDialog(frame) == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) {
panel_1.ReadImageFile(dialog.getSelectedFile().getPath());
panel_1.repaint();
}
}
});
// 実行環境OSにあったUIを適用する
try {
// UIManager.setLookAndFeel("com.sun.java.swing.plaf.gtk.GTKLookAndFeel");
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName());
// SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(panel);
SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(frame);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
// メイン ダイアログの表示
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
ビットマップ描画のためのクラス
public class GraphicsJPanel02 extends JPanel {
private Image image;
public GraphicsJPanel02() {
super();
// ダミーの初期画像
image = CreateBlankImage();
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
// TODO 自動生成されたメソッド・スタブ
super.paintComponent(g);
// 画面縦サイズを固定してスケーリングした幅を算出
int h = (int) ((double) image.getHeight(null)
/ (double) image.getWidth(null) * this.getWidth());
// 画面横サイズを固定してスケーリングした高さを算出
int w = (int) ((double) image.getWidth(null)
/ (double) image.getHeight(null) * this.getHeight());
// 画面サイズにマッチする、縦横比を維持したスケーリングで画像を表示する
if (h > this.getHeight())
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, w, this.getHeight(), this);
else
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, this.getWidth(), h, this);
}
public void ReadImageFile(String filename) {
image.flush();
// 指定されたファイル(filename)から画像を読み込んで image に格納する
try {
ImageIcon imageIcon = new ImageIcon(filename);
image = imageIcon.getImage();
} catch (Exception e) {
// エラーの場合(ファイル不存在や、フォーマット異常では例外発生しないようだ…)
image.flush();
image = CreateBlankImage();
} finally {
// 読み込んだ画像のサイズが異常(=エラー)の場合、ダミー初期画像に差し替える
if (image.getWidth(null) <= 0 || image.getHeight(null) <= 0)
image = CreateBlankImage();
}
}
/**
* ダミー初期画像を生成する
*
* @return Image
*/
private Image CreateBlankImage() {
Image imageTemp = new BufferedImage(320, 280,
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Graphics g = imageTemp.getGraphics();
g.setColor(Color.CYAN);
g.fillRect(0, 0, imageTemp.getWidth(null), imageTemp.getHeight(null));
g.dispose();
return imageTemp;
}
}
画像ファイルの読み込みに、ImageIconではなくImageIOを使う場合は、該当部分のソースコードを次のように書き換える。
public void ReadImageFile(String filename) {
image.flush();
try{
image = ImageIO.read(new File(filename));
} catch (IOException | IllegalArgumentException e) {
image.flush();
image = CreateBlankImage();
} finally {
// 読み込んだ画像のサイズが異常(=エラー)の場合、ダミー初期画像に差し替える
if (image == null || image.getWidth(null) <= 0 || image.getHeight(null) <= 0)
image = CreateBlankImage();
}
}